 Macedonia (ancient kingdom).
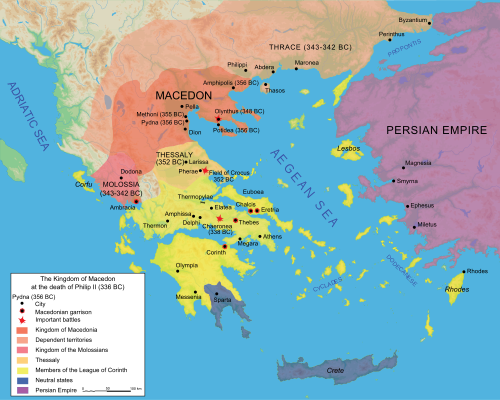
Macedonia (ancient kingdom).Macedonia was an ancient kingdom on the periphery of Archaic and Classical Greece, and later the dominant state of Hellenistic Greece. The kingdom was founded and initially ruled by the Argead dynasty, followed by the Antipatrid and Antigonid dynasties. Home to the ancient Macedonians, it originated on the northeastern part of the Greek peninsula. Before the 4th century BC, it was a small kingdom outside of the area dominated by the city-states of Athens, Sparta and Thebes, and briefly subordinate to Achaemenid Persia. During the reign of the Argead king Philip II (359–336 BC), Macedonia subdued mainland Greece and the Thracians' Odrysian kingdom through conquest and diplomacy, and defeated Athens and Thebes in the Battle of Chaeronea. His son Alexander the Great, commanding the whole of Greece, destroyed Thebes after the city revolted. During Alexander's subsequent campaign of conquest, he overthrew the Achaemenid Empire and conquered as far as the Indus River.

0 comments:
Post a Comment